
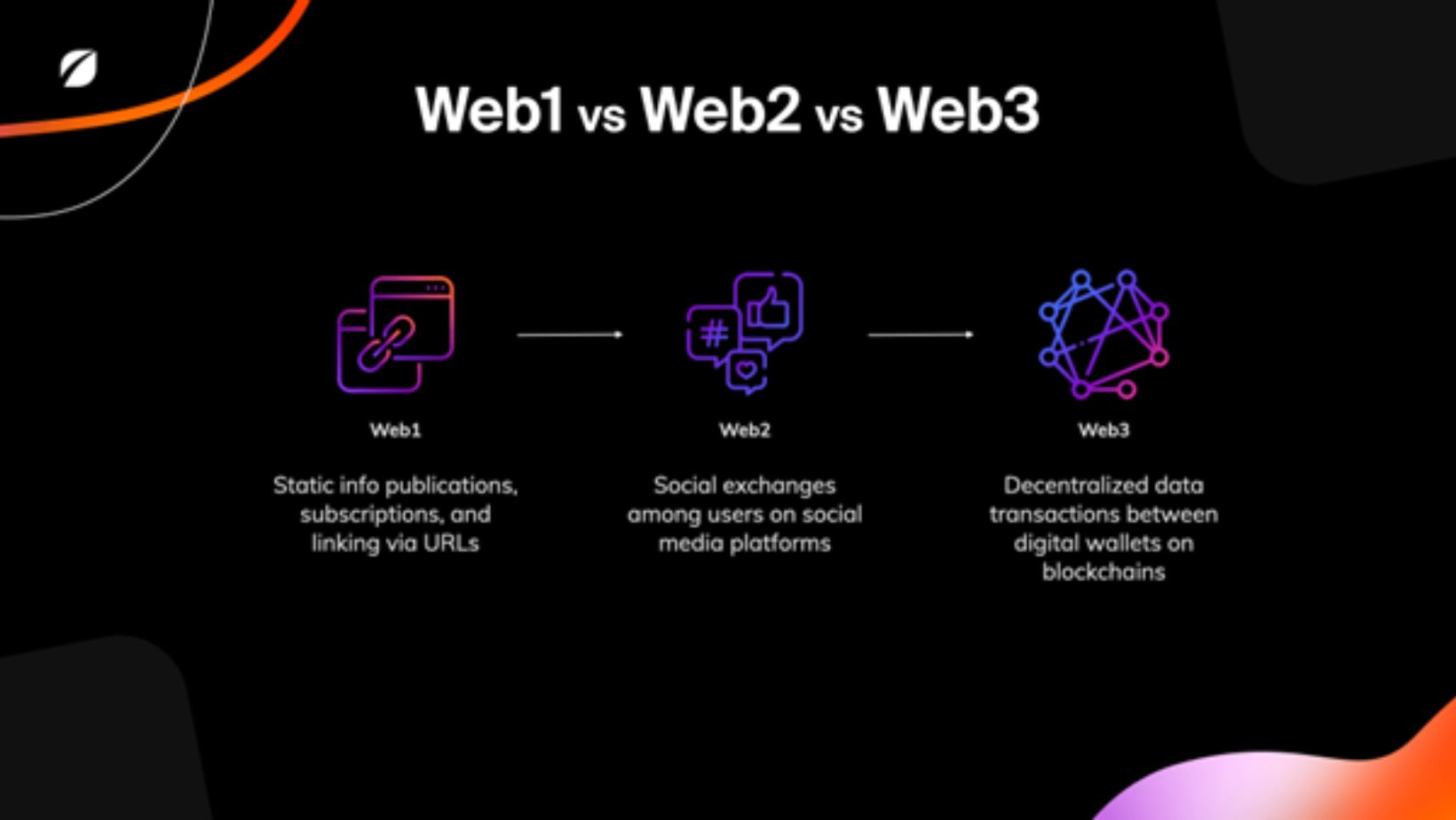
The Internet as we know it today wasn’t always like this. It has experienced an amazing transformation, altering the way we interact, communicate, and contribute. It began as a primitive network of static web pages (Web1) with little interactivity and was mostly used as a digital library. Then came Web2, with dynamic, user-generated content and the growth of social media platforms, which have formed the backbone of our online experiences.
Attention has now shifted to Web3, a new phase that aims to revolutionize the internet by emphasizing decentralization. However, the journey does not end there — concepts such as Web4 and Web5 are already being developed, each offering a unique perspective on the internet’s future. Understanding the difference between Web3 and Web5 is crucial, as these iterations propose distinct models for decentralization, identity, and control over data.
All of us are familiar with Web2 in one way or another. But what exactly is Web3 technology, and how does it pave the way for a more decentralized, user-centric future? How do Web4 and Web5 build on this foundation to create a truly transformative digital landscape? Let’s break down these emerging technologies and their implications for the next iteration of the internet.
What Is Web3 Technology?
To better comprehend Web3, first, let’s explore Web1 and Web2.
Web1: The Era of Static Information
As technical innovation director Elisha Terada describes it, Web1 emerged in the 1990s and was a static websites or blog with read-only content built on systems such as WordPress or Squarespace, where people exchanged content using URLs. Interaction was sparse, and the web served mostly as a digital library or directory.
Web2: The Social Web
Web2, which debuted in the mid-2000s, changed the internet into a hub for social interaction. Platforms such as Instagram, Twitter, and YouTube enabled people to produce, share, and consume content collectively. This data was maintained by centralised technology corporations, who used algorithms to deliver individualised feeds. While Web2 brought communities together, it also raised issues of data privacy and corporate control.
Web3: The Decentralised Web
Web3 represents the next phase of internet evolution, with information connected inside a decentralised public ledger. Unlike Web2’s centralised systems, Web3 uses blockchain technology to provide users with direct control over their data and digital assets. For instance, purchasing an NFT on a blockchain allows you to trace its entire ownership history transparently. Just as Web2 added a social dimension to Web1’s static content, Web3 builds on Web2 by introducing full transparency, user autonomy, and decentralisation.
Three Fundamental Technologies Form the Core of Web3
- Blockchain. It is a distributed digital ledger that guarantees decentralisation, transparency, and immutability of data. Every transaction is kept track of via a network of nodes, recorded on a block, and connected to earlier blocks. This technology supports digital ownership, automated processes, and secure ecosystems, driving the evolution of the internet toward user empowerment and equitability.
- Smart contracts, which are coded automatic agreements that are only carried out when certain criteria are satisfied. These make it possible to interact trustworthy without middlemen.
- Digital assets and tokens: cryptocurrencies, NFTs, stablecoins, central bank digital currencies (CBDCs), and tokenized assets. They permit access to exclusive communities or services, ownership, and trade.
What Are The Practical Applications Of Web3
More than just theoretical growth on the internet, Web3 technology is now transforming businesses and changing the way we use digital technologies. The following are some impressive practical applications using Web3 technology:
1. Decentralised Finance (DeFi)
By avoiding conventional financial intermediaries like banks, Web3 facilitates peer-to-peer (P2P) financial transactions via decentralised platforms. Smart contract-powered services allow users to safely and openly lend, borrow, or trade assets. For instance, token swaps without centralised exchanges are available with Ethereum-based DeFi protocols like as Uniswap.
2. Decentralised Authentication and Identity
Web3 allows people to safely manage their online identities. Decentralised systems of identification provide more privacy by using blockchain technology to authenticate users independently of centralised authority. This guarantees individuals retain control over their personal data while removing threats like data leaks. Here is a short list of available tools.
3. Transparency in the Supply Chain
By offering an unchangeable ledger for tracking products from point of origin to ultimate delivery, blockchain technology improves supply chain management. It is being used by businesses such as Walmart to track the production and delivery of food, guaranteeing its efficiency, safety, and authenticity.
4. Content Ownership and Monetisation
Bypassing intermediaries, Web3 enables content creators to directly commercialise their work. Platforms such as Audius (music streaming and sharing) and Mirror (Web3 publishing) enable tokenisation and micropayments, allowing authors and artists to get just recompense while maintaining ownership of their creative works.
5. Tokenised Real-World Asets (RWA)
Web3 enables fractional ownership and trading by tokenising assets such as commodities, real estate, and artwork. For example, RealT platform tokenises properties, allowing users to exchange their stakes and make smaller real estate investments.
6. Autonomous Decentralised Organizations (DAOs)
DAOs are blockchain-based entities under collective membership governance. Through the application of smart contracts, they enable stakeholders to vote on decisions and proposals. The efficient functioning of decentralised governance in the absence of conventional hierarchies is demonstrated by initiatives such as MakerDAO.
7. Unchangeable Data Retrieval and Storage
Data can be dispersed over a network using decentralised storage solutions like the InterPlanetary File System (IPFS), which makes it resistant to censorship and manipulation. This maintains data integrity while guaranteeing consistency and accessibility.
8. Decentralised Social Media
Social media sites where users maintain control over their information and interactions are supported by Web3. Blockchain-based networks, such as Lens Protocol, allow for transparency in content filtering and provide token awards to encourage user involvement.
9. Global Payments
Web3 makes it easier and cheaper to use cryptocurrency for international transactions. By cutting out intermediaries, blockchain networks reduce costs and processing times, opening up access to financial services in unbanked regions.
10. Integration of IoT and Smart Cities
As blockchain enables decentralised processing of data from IoT devices, it is essential for the development of smart cities. By creating open and secure data exchange ecosystems, blockchain networks are improving the efficiency of services such as energy distribution, traffic management and infrastructure maintenance. 
What Are The Key Principles Of Web3?
Web3 technology is a new revolution instead of just another feature of the worldwide web. It presents ideas and characteristics that go against Web2’s centralised standards. Let’s examine the fundamental features that distinguish Web3 in more detail.
Decentralisation, Openness, and Transparency
Imagine using the internet as an active participant with actual control, rather than merely as a passive consumer. That’s what Web3 promises. This new digital world isn’t dominated by a few tech giants, like its predecessors were. Rather, it is based on blockchain technology, which radically changes the way we communicate online.
Ownership
Do you recall a time when the internet was solely used for reading content? Next came the capacity to produce and distribute. Web3 now presents a ground-breaking idea: genuine ownership. Owning what you produce is more important than simply using or generating. These days, you are basically transferring your rights to large corporations when you generate material or publish on social media.
The Economic Engine
The fundamental idea behind Bitcoin served as inspiration for blockchain networks’ advanced economic models, which today include:
- Reward individuals who contribute to the maintenance of network infrastructure.
- Provide equal and transparent financial incentives.
- Enable decentralized, safe transactions.
Governance
The days of tech platforms making choices behind closed doors are long gone. With Web3’s introduction of decentralized governance, users become decision-makers rather than solely consumers. By adopting advanced tools such as governance tokens, DAOs, collaborative voting mechanisms that ensure that platforms change according to community requirements rather than corporate interests. And users can actively participate in the development of projects.
How Web3 Can Benefit Businesses, And Individuals?
This new iteration of the World Wide Web offers several key benefits for both personal and legal entities:
1. Control Over Data. By removing dependency on centralised organisations like tech giants or social media platforms, Web3 enables participants to own and control their personal data. This lowers the possibility of data exploitation while improving privacy.
2. Decentralised Identity. Web3 provides safe authentication without the need for centralized authorities by allowing users to maintain their digital identities using blockchain-based solutions.
3. Direct Financial Transactions. Peer-to-peer lending, borrowing, and trading without middlemen is possible with decentralised finance (DeFi), which result in reduced costs and easier access to financial services.
4. Monetisation and Access to New Markets. By using tokenization and NFTs, content producers can directly profit from their creations, keeping ownership and taking advantage of fair payment schemes, frequently in the form of micropayments. Companies can engage clients in novel ways and provide new goods and services, including digital assets or unique content.
5. Security and Immutability. Users are shielded from fraud and data tampering by blockchain’s distributed ledger, which guarantees that transactions and data are safe and unchangeable.
6. Increased Transparency. By supplying verifiable product origins in supply chains or guaranteeing data integrity in content creation, blockchain technology enables companies to provide customers with increased transparency.
7. Decentralised Governance. Companies can empower employees, clients, or partners to take part in important company decisions by facilitating collaborative decision-making among stakeholders through decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs).
What Are The Main Differences Between Web2 And Web3?
The ways that Web3 and Web2 handle data, governance, and user interactions are different. Whereas Web3 is user-driven and autonomous, with data saved on decentralised blockchain networks, Web2 is centralised, with restricted data ownership and monetisation by companies. Whereas Web3 removes intermediates and is governed by decentralised autonomous organizations, Web2 uses tokenised incentives, NFTs, or decentralised finance systems to monetise user participation.
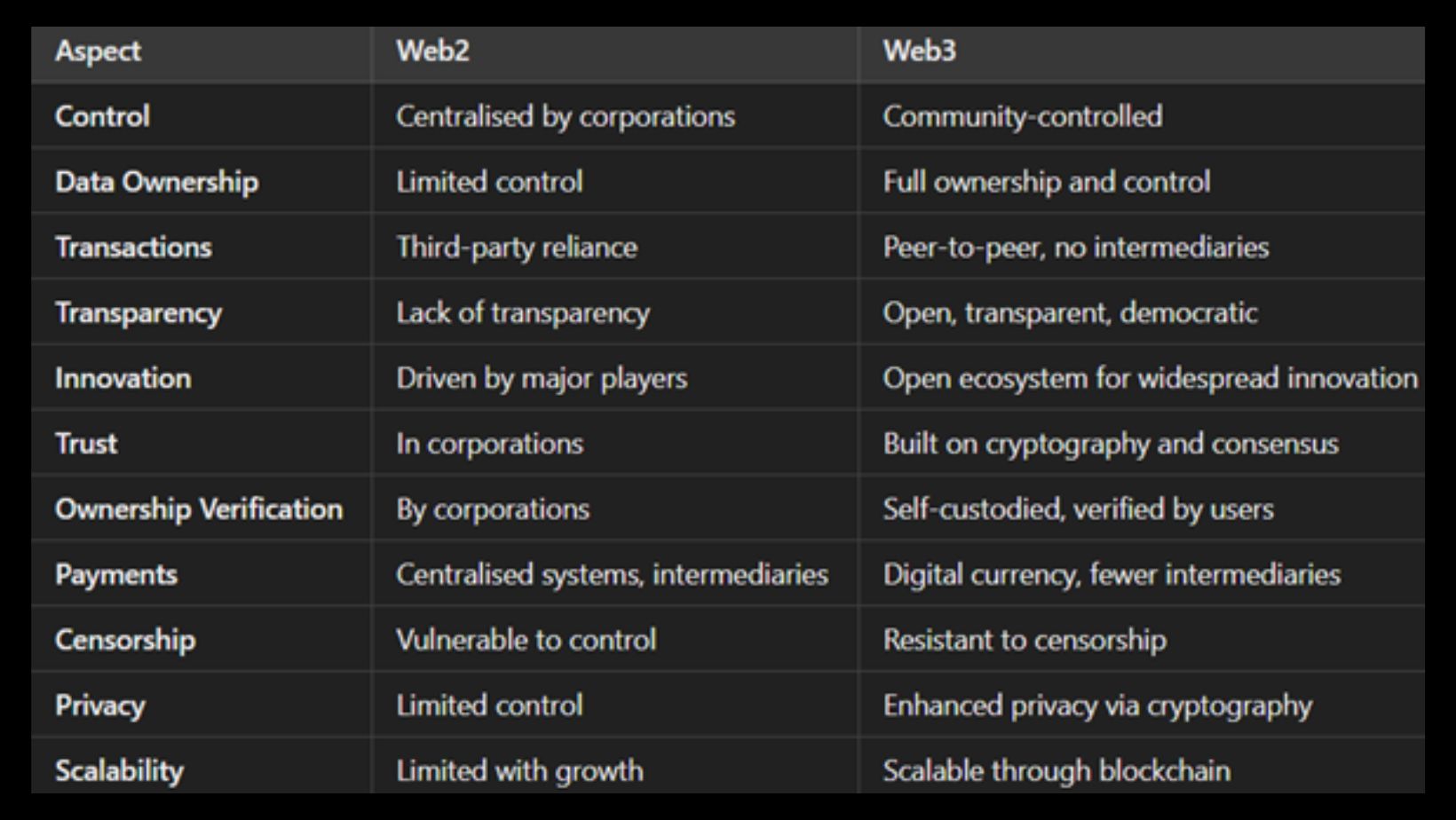
While decentralized systems and cryptographic principles improve security, blockchain’s transparency and consensus procedures build trust.
Additionally, Web3 enables direct user interaction with protocols, encouraging increased autonomy, openness, and creativity.
What Are The Similarities And Differences Between Web3 And Web5?
Web5 is a more comprehensive vision for the internet where the main focus is on decentralised identity, personal data ownership, and privacy, whereas Web3 is concentrated on decentralised apps, smart contracts, and digital assets like cryptocurrencies. By incorporating decentralised identities and offering a completely user-controlled online experience, Web5 expands on the goals of Web3.
But wait. Where is the Web4, you might ask? It is a term proposed by some as the next step in the evolution of the internet, however it lacks a commonly acknowledged or standardised definition, unlike Web3 and Web5. While Web3 focuses on decentralisation via blockchain and Web5 focuses on decentralised identity and full personal data control, Web4 is frequently defined in theoretical terms, and its specific qualities differ depending on who you ask.
Here are Some Concepts About Web4:
AI-Driven Internet
Web4 is envisioned as a fully integrated internet powered by artificial intelligence (AI). In this vision, artificial intelligence (AI) would play an important role in adjusting the internet experience by anticipating user demands, automating procedures, and allowing intelligent devices to connect with users effortlessly.
Full Immersion (Mixed Reality and AR/VR):
Web4 aims to provide a fully immersive digital experience by combining virtual reality (VR) with augmented reality (AR). This might be viewed as a bridge to the metaverse, in which the internet becomes a completely immersive world rather than merely a 2D place.
Autonomous Systems:
Web4 envisions autonomous systems, such as self-learning algorithms and robotics, interacting with the physical world in addition to human-driven digital interactions.
Quantum Computing:
Web4 may incorporate quantum computing to improve data processing, enable real-time AI interactions, and decentralize infrastructures.
So, what is Web5, then?
Unlike Web4, Web5 already has a clear definition. It has been proposed by American Internet entrepreneur, programmer, and a co-founder of Twitter Jack Dorsey in June 2022 as a vision for an ultra-decentralised internet.
In the future, users will have a single, independent identity across all platforms, according to the Web5 idea. This identity provides greater control and privacy because it may be used across several services without losing connections or data. https://youtu.be/KgZYtsj9-V0?feature=shared
Key Pillars of Web5
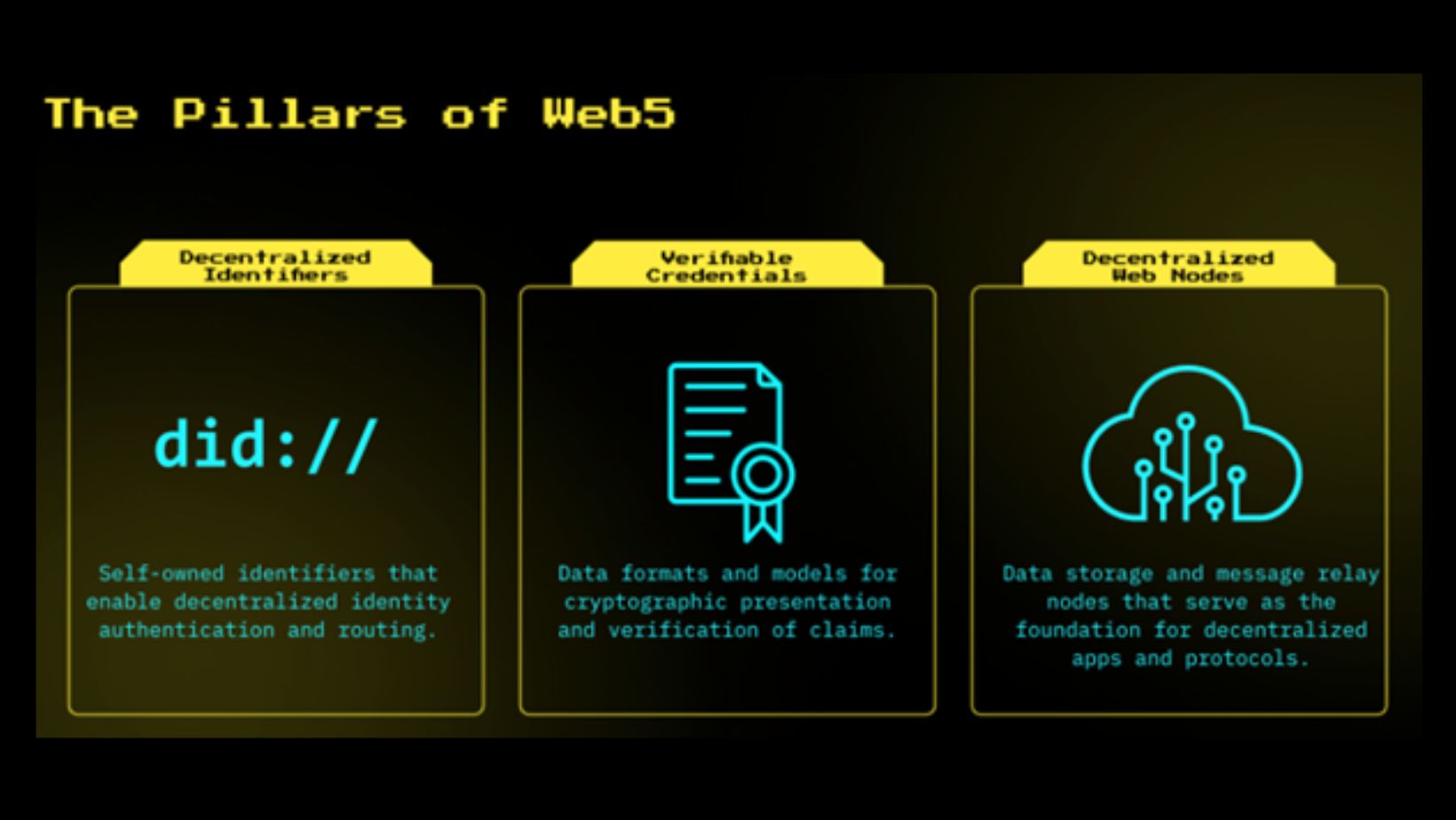
- Decentralised Identifiers (DIDs) allow users to create self-sovereign digital identities that are not controlled by any centralised authority.
- Verifiable Credentials (VCs) enable users to verify their credentials securely and share them when needed without relying on central authorities.
- Decentralised Web Nodes (DWNs) let individuals store and control their own data, eliminating the need for centralised platforms to manage or store user data.
Differences Between Web3 and Web5
- Data Storage. Web3 relies on decentralized off-chain storage, often hosted by third-party platforms like OpenSea or Coinbase. Web5, on the other hand, enables users to host their own data on Decentralised Web Nodes, giving them full control.
- Tokens. While Web3 relies on native tokens for transactions, Web5 does not use or incorporate tokens, focusing more on technology and decentralization rather than financial incentives.
- Applications. Web3 applications or decentralized apps (DApps) are built on blockchain platforms like Ethereum, whereas Web5 decentralised web applications (DWAs) are built around Decentralised Identifiers, interacting with the blockchain when necessary.
Exploring Web3: Challenges, Opportunities, And Future Impact
Web3 is the next logical extension in the evolution of the internet, moving from a centralised, controlled model to a decentralised ecosystem that prioritises user autonomy, privacy, and transparency. Web3 stands out due to its reliance on blockchain technology and empowers users to control their own data and digital identities. While other decentralised technologies like peer-to-peer networks or distributed databases also aim to eliminate central control, Web3’s use of smart contracts, cryptocurrencies, and decentralised finance (DeFi) protocols enables also the creation of an open, user-governed economy. It also functions without relying on intermediaries
What Are the Current Challenges of Adopting Web3 Technology?
It faces a range of hurdles, which include:
- User Adoption. The shift from Web2 to Web3 requires users to understand new concepts such as digital wallets, tokens, and blockchain interactions. User interfaces and experiences are still in the most friendly, making it hard for the average person to engage with Web3 applications.
- Interoperability. With multiple blockchain ecosystems and networks (e.g., Ethereum, Solana, Polkadot), Web3’s fragmented nature presents challenges for applications and services that have to work across different chains.
- Security. As decentralised platforms often put more responsibility on users (e.g., managing private keys and tokens), vulnerabilities and breaches, such as hacks or lost wallets access, present serious risks.
- Scalability. The current state of many Web3 networks, particularly Ethereum, faces scalability issues. Transaction speeds can be slow, and the costs associated with transactions (so-called gas fees) can be ridiculously high, particularly during periods of high network load.
- Energy Consumption. Blockchains like Bitcoin and Ethereum have come under scrutiny for their high energy consumption, with critics arguing that they are not environmentally sustainable.
- Smart Contracts Complexity. Developing smart contracts can be technically challenging. Errors in code can result in significant financial losses or exploitation by malicious actors.
- Legal Uncertainty. There is no clear regulatory framework for Web3 technologies, particularly regarding cryptocurrency transactions and decentralized finance. Governments are still working on creating rules that balance innovation with consumer protection.
- Taxation and Compliance. Issues like token taxation, cross-border transactions, and anti-money laundering (AML) compliance are not well-defined in many countries, making it harder for businesses to navigate Web3 without legal risks.
What Is the Web3 Potential Impact on the Future of the Internet?
This developing technology promises to reshape the internet by creating a more decentralized, user-focused ecosystem. This will lead to:
- Increased Privacy with users controlling their personal data and interactions, reducing the risks associated with data breaches and exploitation.
- Decentralized identity systems enable people to own and control their digital identities, opening the door to more privacy-preserving and equitable internet interactions.
- Decentralised autonomous organisations (DAOs), where decisions are made collectively by token holders, eliminating the need for centralised authorities.
- Advanced monetisation models whereby content creators will be able to directly monetise their work through NFTs, micropayments and token-based rewards, disrupting traditional revenue models that depend on intermediaries.

Individuals can begin by setting up a digital wallet like MetaMask or Trust Wallet to interact with Web3 applications. Explore decentralized applications (DApps) that match your interests, including DeFi platforms, NFT marketplaces, and Web3 social networks. Learning about cryptocurrency is crucial, understanding how tokens power Web3 applications and how to manage them and interact with smart contracts. Businesses should consider integrating Web3 technology into their business model by exploring blockchain-based payments, NFTs, or creating a DAO for community governance. It’s essential to ensure your team understands the regulatory environment surrounding Web3, particularly for DeFi or token-based projects. Start building Web3 applications (DApps) that offer decentralized services to customers, with a strong focus on security and privacy.
In the coming years, Web3 is expected to:
- Get more intuitive and accessible interfaces will likely make Web3 applications more user-friendly.
- Non-fungible tokens (NFTs) will continue to evolve, with more use cases in industries like gaming, digital art, and virtual goods.
- DeFi protocols will grow to include more services like insurance, savings, and investment, potentially displacing traditional financial services.
- We will likely see a more interconnected Web3 ecosystem, where users can easily move assets and information across different blockchains with easy-to-use apps.
Conclusion
Web3 has the potential to rewrite the internet by making it more user-owned, autonomous, and privacy-focused. Even if there are still issues with accessibility, scalability, and regulations, the further advancement of Web3 technologies will likely to open up new business prospects for sectors like content production, gaming, and finance. People and companies should begin investigating how they might take use of these new technologies as Web3 develops further in order to profit from the next chapter of the internet evolution.












